This section includes details about:
- The structure and elements of a Registry entry
- The order in which Registry entries are assigned
- How to search for a Registry entry
- How to add a Registry entry
- How to copy Registry entries to a new group / user
- The Registry cache: Flushing and Enabling / Disabling
- All EMu Registry entries
Overview
EMu is a flexible and extensible application that can be customized with relative ease to suit an institution's requirements. Almost anything in EMu can be customized, from the fields a user is able to view and search, to the uniqueness of a field or combination of fields. The key to EMu's flexibility is its Registry. The EMu Registry stores System configuration information and provides a mechanism for configuring and customizing EMu without the need to reprogram the application. It is used to define site-specific configuration parameters such as:
- EMu's security system, including user and group permissions
- System settings, including locale information and file locations
- MIME types for multimedia resources and conversion information for text-based documents
- Mandatory fields
- Lookup List permissions
- Sort options
- Tab order and display
- Languages in use and general language settings
- Unique values
- Order and appearance of tabs in different modes, e.g. New, Search
- Spell checking options
Registry settings are assigned in a module with a user-friendly interface much like that of any other EMu module.
The Registry module is accessed from the EMu Command Centre by clicking  .
.
Note: By default the Registry module is only accessible to a user with an Administrator account, although Administrators can authorize other users to access the Registry module and to add and edit Registry entries.
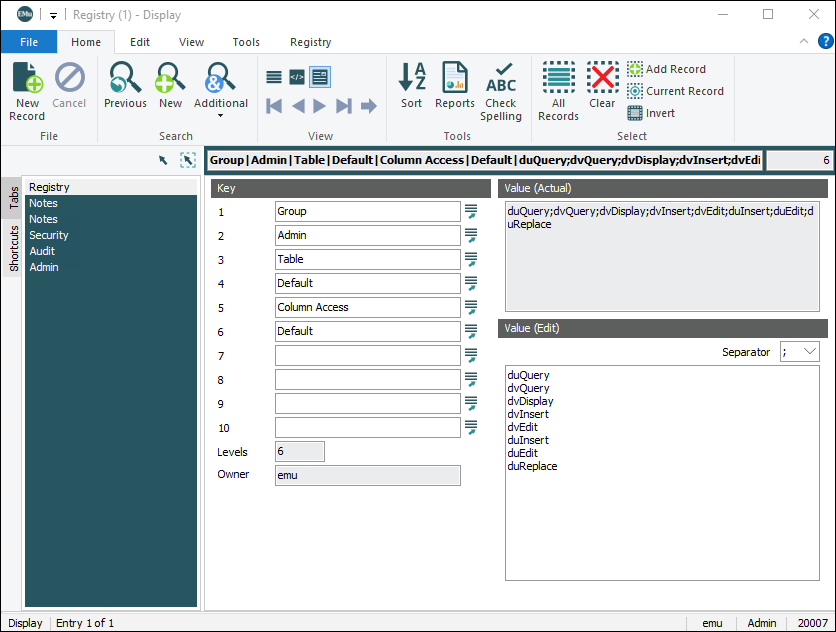
Similar to the Windows Registry, EMu's Registry is a database of configuration entries that comprise a hierarchical key structure with a value:
On the left is a hierarchical sequence of keys with a value entered on the right. There may be up to ten keys in the hierarchy, although most Registry entries use only the first four or five. The value tells EMu which permission, condition or value to apply for the specific circumstance described by the sequence of keys.
Although there is only one value for each Key sequence, the value can be a single value, e.g. true, or it can comprise multiple entries. In the example above, the value is a list of modules that a user can access. In the Registry module, each value is entered one per line.
In the database such multi-value entries are recorded as a string with each value separated by a ; (semicolon) by default:
duQuery;dvQuery;dvDisplay;dvInsert;dvEdit;duInsert;duEdit;duReplace
Almost every operation a user performs in EMu triggers a Registry entry lookup. This occurs behind the scenes and defines what action the System should take depending on the user's privileges, or the System settings.
While there are potentially hundreds of entries to be made in the Registry, for the most part the EMu Administrator only needs to be concerned with two types of Registry entries: System Settings and Table and Column Settings.