Please contact Axiell Support:
- If the Archives utility is not already enabled in your implementation of EMu: some customization of the Catalogue module is required.
- If the Archives utility is already enabled but does not include the new tabs introduced with EMu 6.3, and you would like them implemented:
EMu's Archives utility is an extension of the Catalogue module.
Archival description is the process of capturing, collating, analysing and organizing any information that serves to identify, manage, locate and interpret the holdings of an archival institution and explain the contexts and record systems from which these holdings were selected (Definition from the Society of American Archivists).
There are a number of Archiving standards and EMu's Archives utility has been developed in compliance with:
- ISAD(G) - General International Standard Archival description (Second Edition), maintained by the International Council of Archives (ICA).
- The EAD - Encoded Archival Description - document type definition (DTD), which specifies the elements for description of archival collections. EAD is maintained by the US Library of Congress in partnership with the Society of American Archivists.
The ISAD(G) standard specifies that:
- Archival finding aids (descriptions of archival collections) are hierarchical and multi-level in their structure.
- Levels of description within finding aids should move from a general description of the archive at the highest level to a specific description of each individual 'record' or 'item' at the lowest level of description.
The Standard presents a set of rules for archival description that seeks to:
- Ensure the creation of consistent, appropriate, and self explanatory descriptions.
- Facilitate the retrieval and exchange of information about archival material.
- Enable the sharing of authority data.
- Make possible the integration of descriptions from different locations into a unified information system.
ISAD(G) names 26 elements that archivists can use within their finding aids to record descriptive information. There is a preferred structure for any given description and within the structure the elements are grouped in five (or six) information areas:
- Identity Statement: identifies what is being described and says some significant things about what it is called.
- Context: provides information about the origin and custody of the materials; background, context and provenance.
- Content and Structure: provides information about the subject matter held within the materials, its form, and the way it is arranged.
- Condition of Access and Use: informs users about availability.
- Allied Materials: tells users about other materials that are significant to the ones being described.
- There is a sixth area, Notes, in which anything else of interest not otherwise catered for is placed.
There has been an increasing need for an encoding standard for producing machine readable finding aids that would facilitate distribution of these aids via the internet. This is where the EAD comes in.
The EAD, or Encoded Archival Description, is a developing standard for encoding archive and library finding aids in the form of an SGML DTD (Standard Generalized Markup Language Document Type Definition). SGML is a neutral encoding system that makes it possible to share and reuse information in documents across software applications and across computing platforms.
Like ISAD(G), the EAD assumes that an encoded finding aid consists of hierarchically organized information that describes a unit of records or papers along with its component parts. The EAD standard's document type definition (DTD) specifies the elements to be used to describe a manuscript collection as well as the arrangement of those elements. The EAD tag set has 146 elements and is used both to describe a collection as a whole, and also to encode a detailed multi-level inventory of the collection.
- Official Site of the Encoded Archival Description.
- Encoded Archival Description Tag Library, Version 2002: EAD Elements by Tag Name.
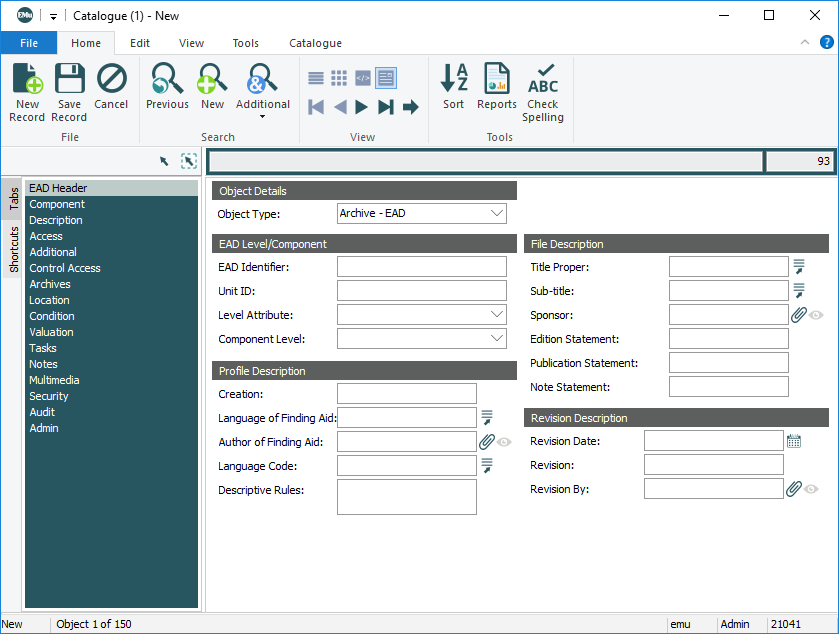
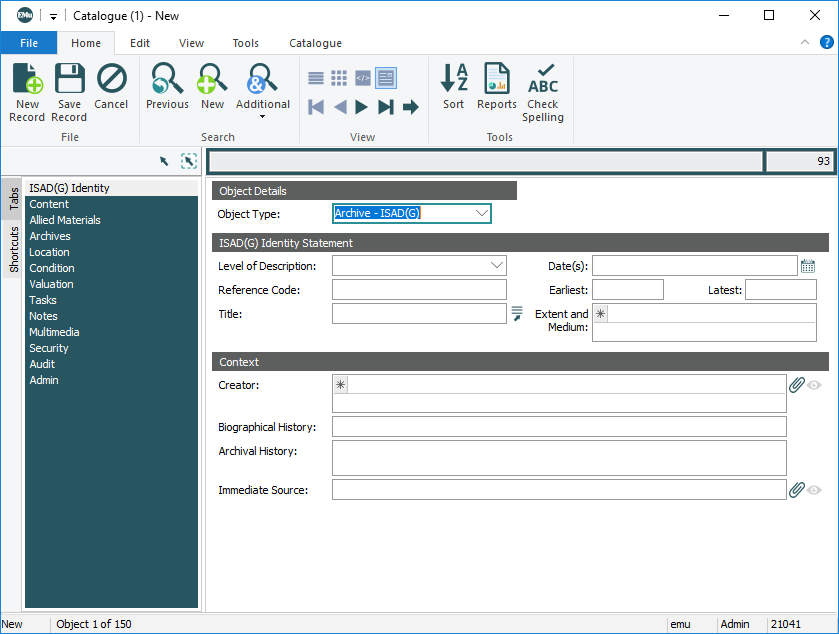
When the Object Type: (Object Details) in the Catalogue module is an archive (e.g. Archive - EAD, Archive - ISAD(G)), various archives tabs are added to the Tabs pane and an Archives tab with commands for working with an archive hierarchy is added to the Ribbon:
You can work with your archives on the Archives tab and / or with the Archives Browse panel. Commands / buttons for manipulating an archives hierarchy are available on the Archives tab itself (buttons to the right of the archive hierarchy) and on the Ribbon. We examine how to use these options here.
In response to a collaborative request from an archives working a number of changes were introduced with EMu 6.3 to improve the management of archives. These include:
- One-step sibling / child record creation for faster Archives hierarchy management.
- An Archival: (Derived Names) field in the Parties module, intended to improve cross-matching terminology with other collections.
Optionally:
- An Accession tab for capturing information needed before or during accessioning and before processing.
- An alternative Control Access tab designed to improve cross-matching terminology with other collections.
Note: Enabling the new tabs in your system will require some modest customization of the Catalogue module by Axiell developers. Please contact Axiell Support before your upgrade for details.
| Tab | Description | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Archives |
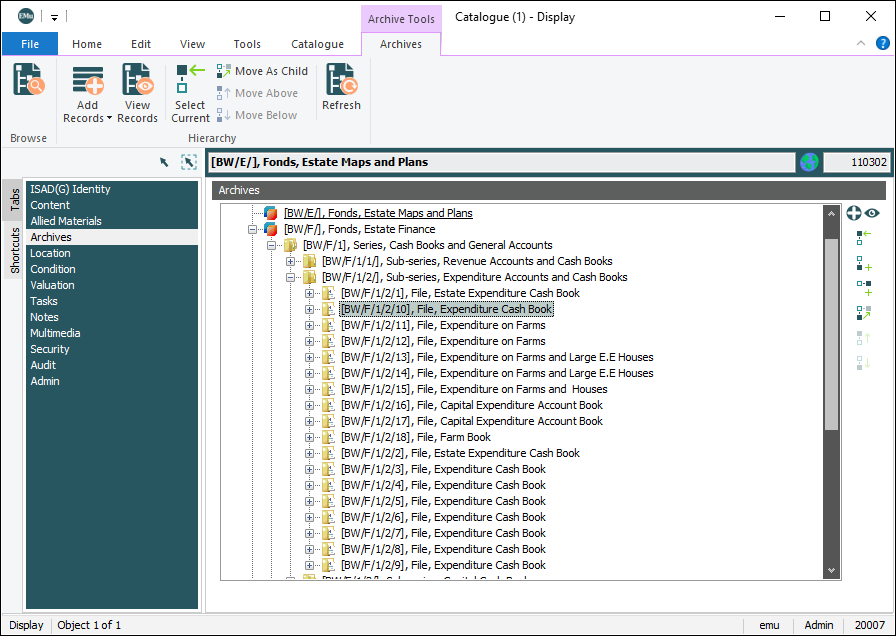
To help visualize the layout of an archive, the Catalogue module includes a tab with a tree view of the structure. The Archives tab displays the hierarchy of the archive with icons used to differentiate between the various levels (fonds, series, etc.): Levels of the repository can be collapsed or expanded as necessary by clicking the Expand There are seven levels to the hierarchy:
The current record, in this case As you move through the Archives hierarchy it is a simple matter to return to the current record
The Archives tab provides functionality to relocate the current record within the hierarchy. For example, the current record can be drag-and-dropped to another position in the hierarchy, a move that shifts the record and all its children to the new location. The Archives tab is sufficient for viewing the structure of the hierarchy for the current record, but it does not provide a simple mechanism for relocating other records within the hierarchy (i.e. records other than the current record), nor does it allow the hierarchy to be restructured easily. To address these two shortcomings and provide a constant visual reminder of the archive hierarchy, EMu includes the Archive Browse panel. See How to work with the Archives hierarchy for details about how to rearrange the hierarchy, add records to the hierarchy and view records in the hierarchy on the Archives tab. |
||||||||||||||||
|
Accession1 |
Record information that is needed before or during accessioning and before archival processing:
Note: This is an optional tab introduced with EMu 6.3. Some customization of the Catalogue module is required to make this tab available. Contact Axiell Support. |
||||||||||||||||
|
EAD |
The numerous EAD wrappers, elements and sub-elements are collected in six tabs according to the EAD standard's broad sections (eadheader, archdesc, etc.) and groups (Profile Description, File Description, etc.). |
||||||||||||||||
|
EAD Header |
Detailed information about each EAD element can be found by following the links below to The Library of Congress definitions: Level / Component
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Component |
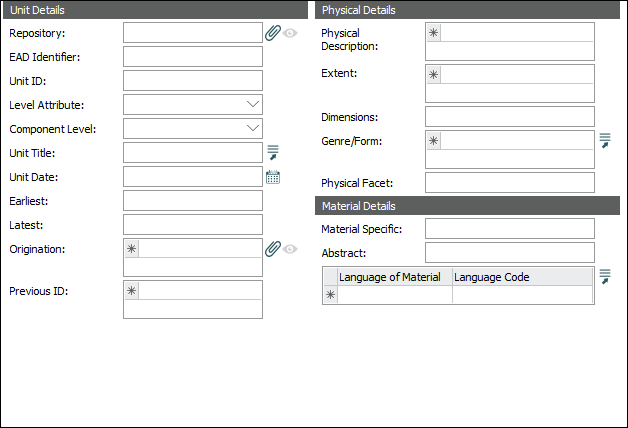
Detailed information about each EAD element can be found by following the links below to The Library of Congress definitions: Unit Details
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Description |
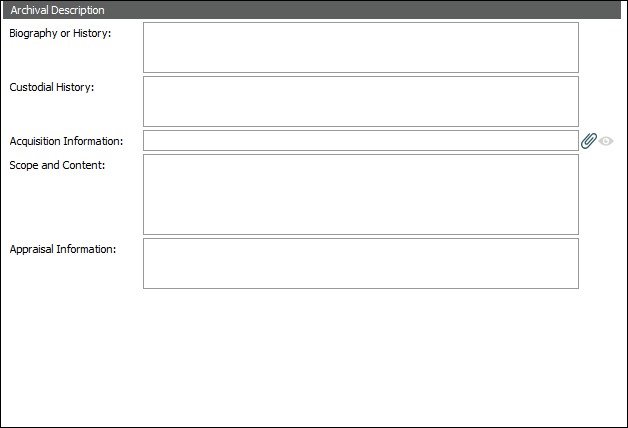
Detailed information about each EAD element can be found by following the links below to The Library of Congress definitions: |
||||||||||||||||
|
Access |
Detailed information about each EAD element can be found by following the links below to The Library of Congress definitions: Access and Use
|
||||||||||||||||
|
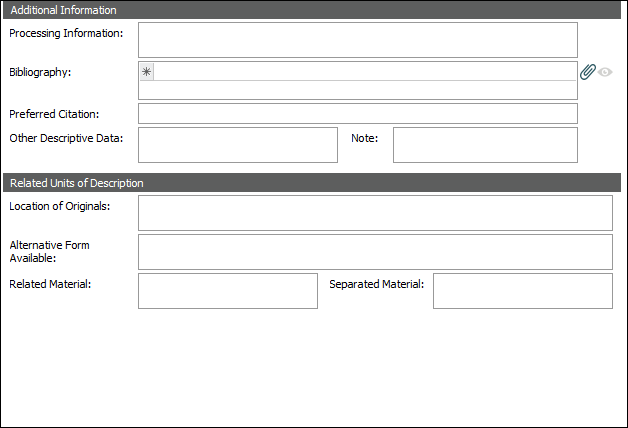
Additional |
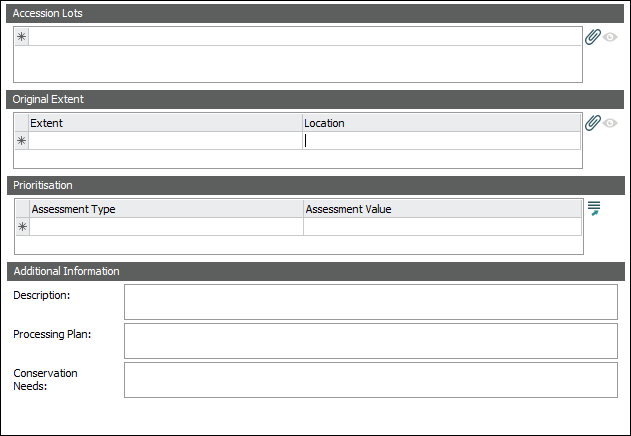
Detailed information about each EAD element can be found by following the links below to The Library of Congress definitions: Additional Information |
||||||||||||||||
|
There are two versions of this tab; only one will be available in your Catalogue module:
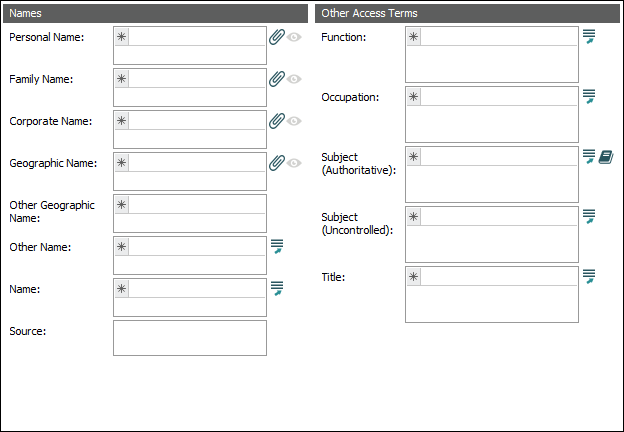
Detailed information about each EAD element can be found by following the links below to The Library of Congress definitions: Names
An alternative version of this tab was introduced with EMu 6.3. Rather than only using Lookup Lists to record names and geographical locations, a number of name fields attach to records in the Parties and Sites modules. An additional Subject field linked to the Thesaurus has been added:
Note: Some customization of the Catalogue module is required to make this alternative version of the Control Access tab available. Contact Axiell Support. |
|||||||||||||||||
|
ISAD(G) |
The 26 elements of the ISAD(G) standard are collected in three tabs, across seven areas:
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Identity |
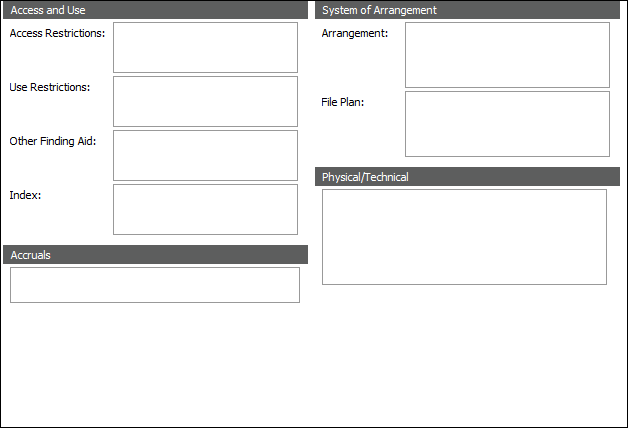
ISAD(G) areas and the relevant ISAD(G) reference: Identity Statement (3.1):
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Content |
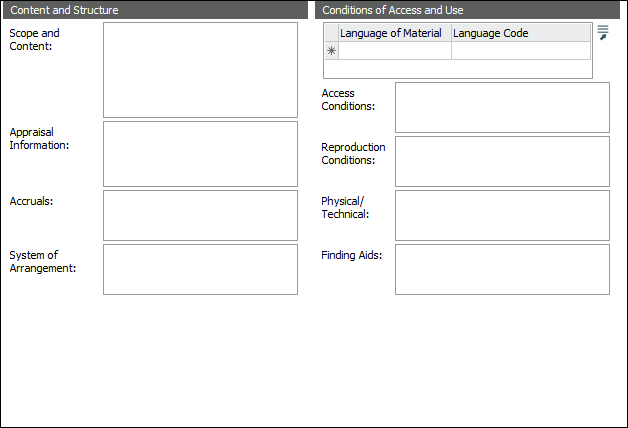
ISAD(G) areas and the relevant ISAD(G) reference: Content and Structure (3.3):
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Allied Materials |
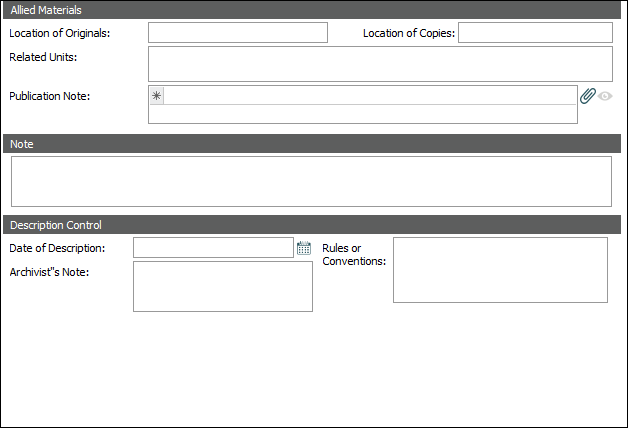
ISAD(G) areas and the relevant ISAD(G) reference: Allied Materials (3.5)
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Relationships |
|||||||||||||||||
|
Location |
|||||||||||||||||
|
Condition |
|||||||||||||||||
|
Valuation |
|||||||||||||||||
|
Tasks |
See Tasks tab for details. |
||||||||||||||||
|
Notes |
See Notes tab for details. |
||||||||||||||||
|
Multimedia |
See Multimedia tab for details. |
||||||||||||||||
|
Security |
See Security tab for details. |
||||||||||||||||
|
Audit |
See Audit tab for details. |
||||||||||||||||
|
Admin |
See Admin tab for details. |


 icon beside a Level.
icon beside a Level. button beside the Archives hierarchy.
button beside the Archives hierarchy.